RIMBAA: UMCG
This page uses terminology as defined in this whitepaper.
- From the RIMBAA 201105 Minutes Orlando
- A templated RIMBAA CDR for a Hospital Wide Continuity of Care Record (Michael van der Zel, see http://www.hl7.org/documentcenter/public/wg/java/RIMBAA_Impl_Aspects_2011_may_WGM_MZ.pdf for his presentation.)
- Simple CRUD CDR at UMCG, static storage is easy, the dynamic behaviour is where the fun/trouble starts, report on issues we ran into creating the CDR store. And the hybrid SQL+XML database solution applied. Plus, a discussion type of presentation were he wants to point out the Research specific issues @ LifeLines/Target
- Michael created a RIM based system for a large (about one million patients) system in the Netherlands. (UMCG). It is a continuity of care system. He didn't start with the Java SIG but developed the system from scratch. They were required to use SQL server. At first they used a pure RIM relational database but found it was too complex for the developers (who were not familiar with RIM), and it did not perform well.
- On a second attempt they used a more constrained RMIM specific database which was adequate and more understandable to the developers. Later experimentation proved that a third method of persistence was even better for the developers and for performance. This is an XML approach where the entire continuity of care instance is stored as an XML blob in the database. There are indexes that allow for querying of sub parts fo the whole document. This solution scales and is in production in this fairly large system.
Presentations
Approach
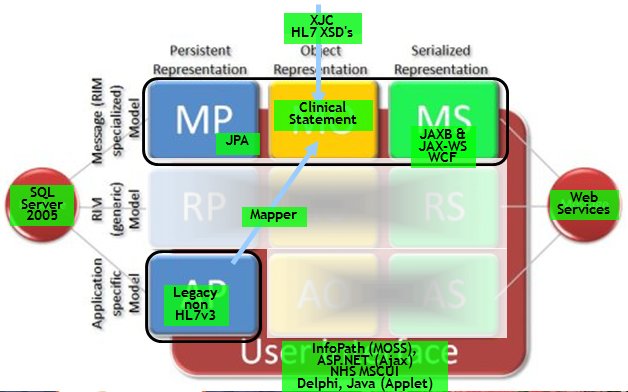
The UMCG approach is the MR-MO-MS path. Some RMIMs with some CMETs make up the Information Model on witch the services are based, it is also used as internal models in the applications. Existing (legacy) systems are mapped using the AR-MO-MS path.
Voor de MR-MO stuk gebruiken we ORM.
- voor ORM gebruiken we de Java Persistance API
- maar ook in .Net hebben we zoiets (ik weet niet meer hoe die heet, geen bekende)
Voor MO-MS gebruiken we webservices, JAX-WS (Java6 implementatie van WebServices) en die gebruikt weer intern JAXB (Java API for XML Binding).
Voor AR-MO gebruiken we nu custom code. De AR onsluiten we via XML DataSets en die mappen we weer op de MO. Voor AR-MO willen we wel graag een standaard tool gebruiken zoals Progress DataXtend Semantic Integrator (zie ook de presentatie!) of BEA AquaLogic Data Services (heb ik inmiddels ook presentatie van).
User Interfaces
UMCG generates user interfaces based on (template) R-MIMs:
- Starting point for the development process are R-MIMs, a template (LIM) derived/specialization of the clinical sattement model.
- These v3 templates are imported into "InfoPath Template Parts", which subsequently are subject to the following:
- Tweak v3 datatype support and other XML schema issues. InfoPath itself isn't v3 data type aware.
- Add look & feel - the HL7 models itself have no L&F,
- Associate coded attributes with value sets for testing. Based on CTS. Using this the ComboBox/List/Checkbox lists can be displayed using the appropriate codes. Code tables exist for departments, specialties, LOINC, and Apelon (SNOMED).
- Add WebService calls to pre-populate elements that already have a value from the clinical data repository.
- The "InfoPath Template Parts" are subsequently used as building blocks to create a form (a user interface).
The relationship between [as well as internal to] the "InfoPath Template Parts" (act relationships in the original v3 model), are not visible to the end user. The layout of the document implicitely documents (informs) the user about the relationships.
Notes
- Binding CUI components to HL7 v3
- Widgets based on HL7 v3 Templates, HL7 v3 CDR (Clinical Data Repository) and CUI
- Detailed Clinical Models