Difference between revisions of "Transmission Pattern"
Rene spronk (talk | contribs) (create new pages for specialized transmission patterns) |
Rene spronk (talk | contribs) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{INM Workitem}} | ||
A Transmission Pattern is a sequence of interactions which are related, | A Transmission Pattern is a sequence of interactions which are related, | ||
and where the relationship is explicitely conveyed within the | and where the relationship is explicitely conveyed within the | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
that the receiver has to respond to the interaction with a specific | that the receiver has to respond to the interaction with a specific | ||
response interaction) then the receiver generates and sends the response | response interaction) then the receiver generates and sends the response | ||
| − | Transmission. The timing and delivery method of the [[Response Transmission]] depends on settings as provided by the Sender with the | + | Transmission. The timing and delivery method of the [[Response Transmission]] depends on settings as provided by the Sender with the initial Transmission. Both the timing (e.g. Immediate vs. Deferred) as well as the delivery method (e.g. Batched, Queued/Polling, Message-Transmission based) are irrelevant when considering Transmission Patterns. |
| − | initial Transmission. | ||
=== Notes === | === Notes === | ||
#The link between the initial interaction and the responses related thereto is established by means of the Acknowledgement/TargetTransmission.id attribute of the [[Transmission Wrapper]]. | #The link between the initial interaction and the responses related thereto is established by means of the Acknowledgement/TargetTransmission.id attribute of the [[Transmission Wrapper]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Examples === | === Examples === | ||
| − | If an Order interaction is sent, which requests an [[Accept Level | + | If an Order interaction is sent, which requests an [[Accept Level Acknowledgement]], and which carries [[Receiver Responsibilities]], then the Order, it's Accept level Acknowledgement, and the interaction sent as a result of the Receiver Responsibilities belong to one and the same |
| − | Acknowledgement]], and which carries [[Receiver Responsibilities]], then | ||
| − | the Order, it's Accept level Acknowledgement, and the interaction sent | ||
| − | as a result of the Receiver Responsibilities belong to one and the same | ||
Transmission Pattern. | Transmission Pattern. | ||
| Line 84: | Line 33: | ||
is not part of the same Transmission Pattern. It is actually the initial | is not part of the same Transmission Pattern. It is actually the initial | ||
interaction of a new Transmission Pattern. | interaction of a new Transmission Pattern. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Specialized Transmission Patterns == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The generic transmission pattern described above is futher specialized for a number of very specific use-cases: | ||
| + | *[[Query Transmission pattern]]: queries, responses and query continuations | ||
| + | *[[Batch Transmission Pattern]]: batches, responses to batches, batch as a response to a query message | ||
| + | *[[Polling Transmission Pattern]]: polling of transmission held on queue | ||
| + | *[[Event Replay Transmission Pattern]]: replaying of historic events by means of new transmissions | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Message Exchange Patterns (MEP) == | ||
| + | The concept of Transmission Pattern is the equivalent of a WSDL Message Exchange Pattern (MEP), See [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Message_Exchange_Pattern Wikipedia] or [http://www.w3.org/TR/soap12-part1/#soapmep W3C] for details. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Almost all HL7 transmissions map to a [[One Way MEP]] between a [[Source]] and a [[Destination]]. The only exception to the rule is a transmission that results in an immediate response transmission: this maps to a [[Request/Response MEP]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 09:11, 4 July 2006
A Transmission Pattern is a sequence of interactions which are related, and where the relationship is explicitely conveyed within the Transmission Wrapper.
Contents
Generic Transmission Pattern
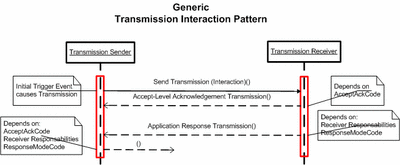
The figure contains a description of the generic HL7 Transmission interaction pattern. The Transmission Sender (an HL7 Application) sends the initial Transmission. The Transmission Receiver (another HL7 Application) performs an accept-level validation, and sends an accept-level acknowledgement transmission if the Sender had requested such an acknowledgement.
If the initial Transmission is an interaction which has Receiver Responsibilities associated with it (i.e. the HL7 standard specifies that the receiver has to respond to the interaction with a specific response interaction) then the receiver generates and sends the response Transmission. The timing and delivery method of the Response Transmission depends on settings as provided by the Sender with the initial Transmission. Both the timing (e.g. Immediate vs. Deferred) as well as the delivery method (e.g. Batched, Queued/Polling, Message-Transmission based) are irrelevant when considering Transmission Patterns.
Notes
- The link between the initial interaction and the responses related thereto is established by means of the Acknowledgement/TargetTransmission.id attribute of the Transmission Wrapper.
Examples
If an Order interaction is sent, which requests an Accept Level Acknowledgement, and which carries Receiver Responsibilities, then the Order, it's Accept level Acknowledgement, and the interaction sent as a result of the Receiver Responsibilities belong to one and the same Transmission Pattern.
If the Order results in an Observation interaction then that interaction is not part of the same Transmission Pattern. It is actually the initial interaction of a new Transmission Pattern.
Specialized Transmission Patterns
The generic transmission pattern described above is futher specialized for a number of very specific use-cases:
- Query Transmission pattern: queries, responses and query continuations
- Batch Transmission Pattern: batches, responses to batches, batch as a response to a query message
- Polling Transmission Pattern: polling of transmission held on queue
- Event Replay Transmission Pattern: replaying of historic events by means of new transmissions
Message Exchange Patterns (MEP)
The concept of Transmission Pattern is the equivalent of a WSDL Message Exchange Pattern (MEP), See Wikipedia or W3C for details.
Almost all HL7 transmissions map to a One Way MEP between a Source and a Destination. The only exception to the rule is a transmission that results in an immediate response transmission: this maps to a Request/Response MEP.