Difference between revisions of "Fulfillment Manager Conceptual Specification"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
===Service Description and Purpose=== | ===Service Description and Purpose=== | ||
| + | The Orders Fulfillment Service provides access to information regarding the fulfillment(s) of clinical services. It is separate and distinct from the actual capability services that: | ||
| + | *support clinical processes (including but not necessarily limited to Labs, Images, and Consults) | ||
| + | *the actual management of the Order Request itself | ||
| + | *the actual delivery of information obtained in clinical processes and ordered via Order Requests. | ||
| + | This service is leveraged by the Request and Fulfillment Interoperability Pattern. It provides a consistent means of integrating certain capabilities between the components of a dispersed healthcare team working with different infrastructures, systems, standards, and business processes. | ||
===Scope=== | ===Scope=== | ||
| − | + | The Order Fulfillment Service describes a number of discrete steps in managing the fulfillment portion between members of a healthcare team that support request and fulfillment. Since these steps are common regardless of clinical service offered, they help to form a consistent pattern of behavior that may be applied in many situations. In so doing, the OF Service distinguishes between the order for a lab test, the promise of fulfillment, and the lab test itself, which may have a different lifecycle or which may serve a broader audience. | |
| − | |||
===Reason why the service is necessary=== | ===Reason why the service is necessary=== | ||
| − | + | The Order Fulfillment Service provides a key integrating component between systems involved in the distributed practice of patient-centric clinical care. It allows various systems performing clinical services to negotiate the fulfillment of requests for those services. This in turn provides a decoupling for these systems from the business processes invoked by healthcare practitioners. This separation of concerns also provides a clear boundary not only for its own capabilities, but for organizations engaged across organizational boundaries that need to share the business processes around request and fulfillment. | |
| − | + | Thus, for example, the Order Fulfillment Service enables a lab to operate completely independently from the Order Request system, and for the management of the clinical process to be managed separately from the financial management process that may happen in parallel. Additionally, this separation can happen at an institution or across several institutions or facilities. | |
==Structure of the Service== | ==Structure of the Service== | ||
Revision as of 00:42, 27 November 2012
Link back to solution specification
Contents
Overview
Service Description and Purpose
The Orders Fulfillment Service provides access to information regarding the fulfillment(s) of clinical services. It is separate and distinct from the actual capability services that:
- support clinical processes (including but not necessarily limited to Labs, Images, and Consults)
- the actual management of the Order Request itself
- the actual delivery of information obtained in clinical processes and ordered via Order Requests.
This service is leveraged by the Request and Fulfillment Interoperability Pattern. It provides a consistent means of integrating certain capabilities between the components of a dispersed healthcare team working with different infrastructures, systems, standards, and business processes.
Scope
The Order Fulfillment Service describes a number of discrete steps in managing the fulfillment portion between members of a healthcare team that support request and fulfillment. Since these steps are common regardless of clinical service offered, they help to form a consistent pattern of behavior that may be applied in many situations. In so doing, the OF Service distinguishes between the order for a lab test, the promise of fulfillment, and the lab test itself, which may have a different lifecycle or which may serve a broader audience.
Reason why the service is necessary
The Order Fulfillment Service provides a key integrating component between systems involved in the distributed practice of patient-centric clinical care. It allows various systems performing clinical services to negotiate the fulfillment of requests for those services. This in turn provides a decoupling for these systems from the business processes invoked by healthcare practitioners. This separation of concerns also provides a clear boundary not only for its own capabilities, but for organizations engaged across organizational boundaries that need to share the business processes around request and fulfillment. Thus, for example, the Order Fulfillment Service enables a lab to operate completely independently from the Order Request system, and for the management of the clinical process to be managed separately from the financial management process that may happen in parallel. Additionally, this separation can happen at an institution or across several institutions or facilities.
Structure of the Service
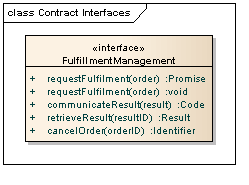
The Fulfillment Manager Conceptual Diagram is shown below. The variation on the RequestFulfillment return value reflects the business flow difference between ambulatory and in-patient labs - in ambulatory, there is no return value, where in-patient returns a Promise.
Assumptions and Dependencies
Comment Upon what services does this specification depend (underpinning infrastructure, other HL7 services, etc. Are there any key assumptions that are being made?
Implementation Considerations
Comment
Relevant and representative examples of deployment scenarios. Consider representation formalism and the intended audience, not necessarily rigorously expressing the content in UML. This specification in the real world (e.g., relationships to existing infrastructure, other deployed services, dependencies, etc.). Consider the ways that information bindings will be realized through the operations. If necessary, outline a strategy for this binding.
Detailed Functional Model for Each Operation
Request Fulfillment
- Description: Allows an order manager to request fulfillment of an order
- Pre-Conditions:
- The client has sufficient information to create the request
- User or requestor has permissions to create a request within the context
- Conceptual Information Objects
- Inputs: Order
- Outputs: Promise
- Post-Conditions:
- Exception Conditions: None identified
- Aspects left for Technical Bindings (optional)
- Reference to Functional Profiles (optional)
- Notes
Communicate Result
- Description: Allows the fulfill to communicate a result to the requestor. This is a conceptual operation representing the "push" of a result from the Fulfiller to the Orderer - at the logical level it would be represented by several operations based on the message exchange pattern.
- Pre-Conditions:
- A Result (preliminary or final) is available to be communicated to the orderer
- Conceptual Information Objects
- Inputs: Result
- Outputs: Code
- Post-Conditions:
- Result has been communicated and the receipt acknowledged
- Exception Conditions:
- Aspects left for Technical Bindings (optional)
- Reference to Functional Profiles (optional)
- Notes
- This is a conceptual operation representing the "push" of a result from the Fulfiller to the Orderer - at the logical level it would be represented by several operations based on the message exchange pattern.
Cancel Order
- Description: Used when a requstor (placer) would like for a previously requested, and not yet completed, order to not be performed.
- Pre-Conditions:
- An order exists and the identifier is known
- The order is not completed
- The user or requestor has permission to update an order
- Conceptual Information Objects
- Inputs: Order, Order Identifier
- Outputs: Order
- Post-Conditions:
- The order referenced by order identifier has been cancelled and will not be acted upon.
- The cancel order identifier is returned
- Exception Conditions:
- Order is not known to the fulfiller
- Order has already been completed
Retrieve Result
- Description: Allows a requestor to retrieve a result from the fulfiller with using the result identifier
- Pre-Conditions:
- The result identifier has been previously communicated to the fulfiller.
- Conceptual Information Objects
- Inputs: Result Identifier
- Outputs: Result
- Post-Conditions
- Exception Conditions
- Aspects left for Technical Bindings (optional)
- Reference to Functional Profiles (optional)
- Notes
Profiles
Introduction
Functional Profiles
Information Profiles
Comment
- describe any information profiles applicable to this service, and the related state transitions
Recommendations for Conformance and Compliance
These will be elaborated in the next round of specification development