Permissions Catalog: Recommendations for Reuse
The current Permissions Catalog for Role-Based Access Control specifies a set of normative permissions that specify operations that may be applied to a variety of object types.
The permission catalog is a normative specification and it is available for download.
- The most recently published permission catalog is 20071112_HL7_RBAC_Healthcare_Permission_Catalog_v3_37.pdf
The operations refer to the ability to:
- append,
- create,
- read,
- update,
- delete, and
- execute
specific "objects" identified in the RBAC standards. The "objects specify:
| Permission | ||
|
Operation |
Object |
Effect |
|
append |
Administrative Ad-hoc Report |
A role that has this permission, allows the user that logs in with that role to append information to an existing ad-hoc administrative report. |
Healthcare Operations rather RBAC Operations
The healthcare work flow as specified in HL7, provides for "trigger events" that correspond to healthcare-specific operations:
| HL7 Operations (trigger event) | RBAC Operations |
| create | create |
| revise | update,append |
| activate | NA |
| complete | execute(?) |
| suspend | NA |
| resume | NA |
| abort | NA |
| hold | NA |
| release | NA |
| cancel | NA |
| obsolete | NA |
| nullify | delete(?) |
| NA (to be added to HL7 along with other triggers for Composite Privacy Consent Directive) | read |
The following diagram shows the trigger events and the states that correspond to the healthcare work flow for healthcare object (e.g. Act). For example, an order may be created, activated, then canceled. Similarly an order may be created, activate, revised, and eventually completed.
The following diagram is an extract from HL7 RIM reference documentation and illustrates how HL7 defines "healthcare trigger events" and it illustrates that the objects
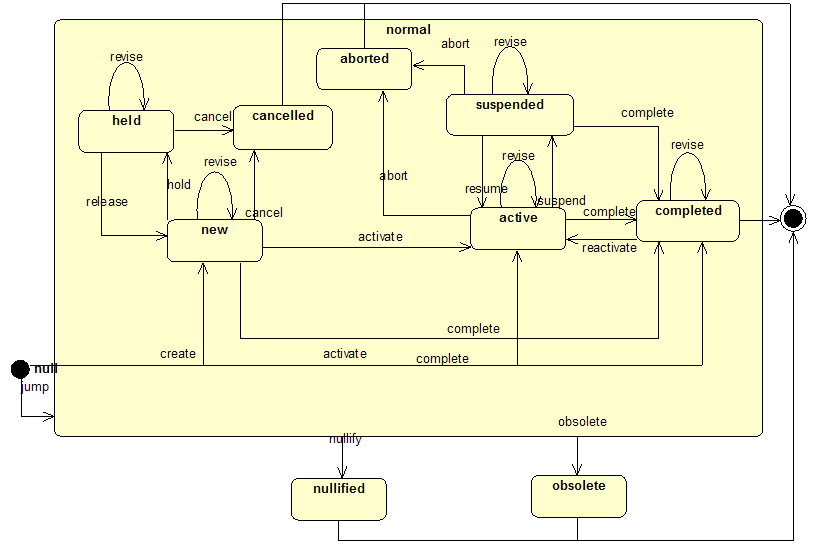
States of Act:
- aborted (sub-state of normal): The Act has been terminated prior to the originally intended completion.
- active (sub-state of normal): The Act can be performed or is being performed.
- cancelled (sub-state of normal): The Act has been abandoned before activation.
- completed (sub-state of normal): An Act that has terminated normally after all of its constituents have been performed.
- held (sub-state of normal): An Act that is still in the preparatory stages has been put aside. No action can occur until the Act is released.
- new (sub-state of normal): An Act that has been activated (actions could or have been performed against it), but has been temporarily disabled. No further action should be taken against it until it is released.
- normal: Encompasses the expected states of a service object, but excludes "nullified" and "obsolete" which represent unusual terminal states for the life-cycle.
- nullified: This Act instance was created in error and has been 'removed' and is treated as though it never existed. A record is retained for audit purposes only.
- obsolete: This Act instance has been replaced by a new instance.
- suspended (sub-state of normal): Active service object is temporarily suspended.
State transitions of Act:
- abort (from active to aborted)
- revise (from active to active)
- complete (from active to completed)
- suspend (from active to suspended)
- reactivate (from completed to active)
- revise (from completed to completed)
- cancel (from held to canceled)
- revise (from held to held)
- release (from held to new)
- activate (from new to active)
- cancel (from new to canceled)
- complete (from new to completed)
- hold (from new to held)
- revise (from new to new)
- nullify (from normal to nullified)
- obsolete (from normal to obsolete)
- activate (from null to active)
- complete (from null to completed)
- create (from null to new)
- jump (from null to normal)
- abort (from suspended to aborted)
- resume (from suspended to active)
- complete (from suspended to completed)
- revise (from suspended to suspended)
