Difference between revisions of "Communication Process Model"
Rene spronk (talk | contribs) |
Rene spronk (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
Note also that this also might have repercussions for the "duplication" item at MCCI item lists. Is there a difference if the message is "duplicated" at the Transmission.id and ControlAct.id level? | Note also that this also might have repercussions for the "duplication" item at MCCI item lists. Is there a difference if the message is "duplicated" at the Transmission.id and ControlAct.id level? | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Business-Level Receiver Resonsibilities == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The question pharmacy and lab are faced with seems to boil down to this example use-case: how do I send (1) "here's an order, please perfom" v. (2) "FYI: here's an order, please keep on record, do not perform". | ||
| + | *Let's assume the receiver responsabilities (from a pure communications standpoint) are the same, and that both interactions (1) and (2) are notifications that DO NOT have receiver responsabilities. (i.e. no application-level accepts or rejects) | ||
| + | *In that case interaction (1) has the same structure, trigger event, and (communication-level) receiver responsabilities as interaction (2). So currently in v3 modeling terms they are exactly the same. | ||
| + | *So we have a use-case for wishing to explicitely include some of the "business level receiver responsabilities" of the receiver into the interaction, e.g. "this is an order I want you to act upon" v. "FYI, do nothing". | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Tom de Jong): The example use-case states that the interactions do not have receiver responsibilities, but that's not entirely true. [[Receiver Responsibilities]] have two (potential) elements: | ||
| + | #the required response interactions (communication responsibilities) and/or | ||
| + | #the required resulting trigger events (processing responsibilities). Of course the trigger event and the interaction will often go hand in hand, but in this example we assumed there were no communication responsibilities. | ||
| + | |||
| + | So the first question is: can the difference between the two interactions be determined by the fact that one will result in a trigger at the receiver (the request for fulfilment) and the other will not (the notification)? So in this example, without a response interaction, what is the resulting trigger event (so, on the receiver side) for the fulfilment request? | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Rene) One of the problems when discussing this is that the definition of [[Receiver Responsibilities]] has never been formally agreed upon. There is a working definition, but it contains a definition of [[Trigger Event]] that is purely communication oriented, not business process oriented. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Lloyd)We need to discuss within MnM whether introducing a level of standardization above the existing level of "receiver responsibilities" is desirable. Effectively what we'd be doing is defining part of the 'internal' state machine of the various application roles and showing how a complete flow might occur. This gets into the area of application behavior, which is an area where HL7 has traditionally tread very lightly. (Rene) This additional level is currently labeled [[Interaction Pattern]] on this Wiki. | ||
[[Category:INM Glossary]] | [[Category:INM Glossary]] | ||
Revision as of 20:08, 7 May 2006
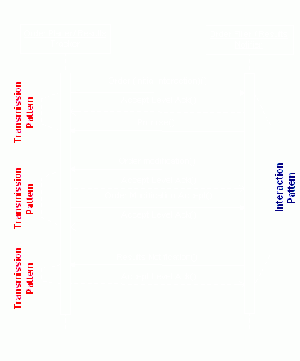
Glossary definition: An Interaction Pattern is a sequence of interactions that are related because they belong to one and the same business process.
Details
An Interaction Pattern consists of 1 or more Transmission Patterns. The interactions may be linked by business process identifiers such as "Placer Order ID", "queryId", "PrescriptionID".
At this level of abstraction the delivery method of the interactions is of no relevance whatsoever.
- The use of some Interactions (e.g. Accept Level Acknowledgement,
Polling Interaction, Query Continuation/Abort Interaction and Batch Based Interactions) is not relevant for an Interaction Pattern, this is relevant at the Transmission level only.
- Most Storyboard Diagrams in the HL7 v3 standard describe an
Interaction Pattern.
- Interaction Patterns can exist as a definition (a class) as well as a partcular instance of that pattern.
Examples
A Laboratory Order, followed by a Promise, a modification of the Order by the Laboratory, and a final labresult constitutes an interaction. The interaction pattern consists of 3 Transmission Patterns. The initiating interaction of each Transmission Pattern results in messages linked to it by means of the Transmission Wrapper.
Notes
All interactions have to have a payload model, to ensure all interactions contain some form of business-process-identifier, which allows the linking of individual Transmissions within an Interaction Pattern. 20060113: MNM WGM: All app level interactions must have a defined payload model. for simple accept/refusal interactions the payload may be limited to a simple shared message MT referencing the request being accepted/refused. (Rene/Heath, 6-0-2) Ongoing discussion: there are use-cases where a payload may not make sense.
Discussion: How can payload.id be a 'primary' identifier for a business process, when the identifier remains the same across several business processes, and may not even exist at all times through-out the process? Basically we have the following:
- Transmission.id - uniquely identifies a point-to-point hop
- ControlAct.id - uniquely identifies a particular action, which may be a step in a sequence
- Transaction.id (does not yet exist) - uniquely identifies a particular sequence of actions
- Payload.id - uniquely identifies a business object which may be manipulated by 0..* transactions.
(LLoyd) I agree that #1 is pretty useless at the business level. I'd love for us to use #2. I can get talked into supporting #3. I think #4 is as useless for the purposes you're describing as #1 is.
(Miroslav) Just want to suppport Lloyd's suggestion. From the communication dynamics point of view, I don't think that business process id can be contained in Transmission Wrapper. Having it in the Payload also doesn't make sense since this should be fully use case and content oriented. Control Act Wrapper is the single logical place to have the business process identification managed.
Note also that this also might have repercussions for the "duplication" item at MCCI item lists. Is there a difference if the message is "duplicated" at the Transmission.id and ControlAct.id level?
Business-Level Receiver Resonsibilities
The question pharmacy and lab are faced with seems to boil down to this example use-case: how do I send (1) "here's an order, please perfom" v. (2) "FYI: here's an order, please keep on record, do not perform".
- Let's assume the receiver responsabilities (from a pure communications standpoint) are the same, and that both interactions (1) and (2) are notifications that DO NOT have receiver responsabilities. (i.e. no application-level accepts or rejects)
- In that case interaction (1) has the same structure, trigger event, and (communication-level) receiver responsabilities as interaction (2). So currently in v3 modeling terms they are exactly the same.
- So we have a use-case for wishing to explicitely include some of the "business level receiver responsabilities" of the receiver into the interaction, e.g. "this is an order I want you to act upon" v. "FYI, do nothing".
(Tom de Jong): The example use-case states that the interactions do not have receiver responsibilities, but that's not entirely true. Receiver Responsibilities have two (potential) elements:
- the required response interactions (communication responsibilities) and/or
- the required resulting trigger events (processing responsibilities). Of course the trigger event and the interaction will often go hand in hand, but in this example we assumed there were no communication responsibilities.
So the first question is: can the difference between the two interactions be determined by the fact that one will result in a trigger at the receiver (the request for fulfilment) and the other will not (the notification)? So in this example, without a response interaction, what is the resulting trigger event (so, on the receiver side) for the fulfilment request?
(Rene) One of the problems when discussing this is that the definition of Receiver Responsibilities has never been formally agreed upon. There is a working definition, but it contains a definition of Trigger Event that is purely communication oriented, not business process oriented.
(Lloyd)We need to discuss within MnM whether introducing a level of standardization above the existing level of "receiver responsibilities" is desirable. Effectively what we'd be doing is defining part of the 'internal' state machine of the various application roles and showing how a complete flow might occur. This gets into the area of application behavior, which is an area where HL7 has traditionally tread very lightly. (Rene) This additional level is currently labeled Interaction Pattern on this Wiki.