Difference between revisions of "HData"
| (24 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category:Foundational SOA Specifications]] | ||
| + | Return to Main [http://hssp.wikispaces.com SOA WG/HSSP] Page | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| − | hData is a set of specifications that have been developed with ease-of-implementation in mind. | + | hData is a set of specifications that have been developed with ease-of-implementation in mind. hData was first presented to a wider audience within HL7 as the September 2009 meeting in Atlanta, GA. Since then, hData has first been evalauted as a HL7 research project within the [[ITS_WG|ITS working group]]. The research project culminated in a [http://www.hl7.org/ctl.cfm?action=ballots.home&ballot_cycle_id=522&ballot_voter_id=0 "For Comment" ballot] in January 2011. After a carefull analysis, HL7 decided to standardize hData under the leadership of the [[Service_Oriented_Architecture|SOA working group]] with ITS and [[Modeling_and_Methodology|MnM]] as interested parties. |
| + | |||
| + | == Specifications == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Standardization Status === | ||
| + | |||
| + | hData currently consists of two specifications which have both past the initial peer review: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The [http://www.hl7.org/v3ballot/html/infrastructure/hdata/hdatadf.html HL7 hData Record Format V1] specifies how multiple documents (XML and non-XML media types) containing medical data can be hierarchically organized. It allows metadata management per individual document, signature over files, linking of related documents, and defines the items needed to define a complete hData Content Profile (HCP). The current project scope statement is [[media:HData Record Format Project Scope Statement-v2.doc|here]]. The September 2011 DSTU Ballot reconciliation document can be found [[media:V3 ITS HDATA RF R1 D1 2011SEP Consolidated-working copy 20111128.xlsx|here]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The [http://doc.omg.org/health/11-09-04 hData REST Binding for RLUS V1] specifies how a record adhering to the HRF specification can be access through a RESTful approach using HTTP as the transport protocol. It is a [http://www.omg.org Object Management Group] (OMG) specification that was developed by the HL7/OMG [http://hssp.wikispaces.com HSSP collaboration]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Introduction === | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| Line 9: | Line 26: | ||
hData requires strong separation of the technical representation and transport technology on the one side, and the clinical content of an electronic health record on the other side. To this end, hData has the concept of hData Content Profiles (HCP), which define what kind of content is represented and transport through hData. It should be note that conceptually CDA and hData are similar in their approach to representing data points in a hierarchical way. | hData requires strong separation of the technical representation and transport technology on the one side, and the clinical content of an electronic health record on the other side. To this end, hData has the concept of hData Content Profiles (HCP), which define what kind of content is represented and transport through hData. It should be note that conceptually CDA and hData are similar in their approach to representing data points in a hierarchical way. | ||
| − | + | It should be noted that the two specification are not an ITS in the traditional sense, since they do not determine how a logical model is implemented and rendered on the wire. Instead, the HRF organizes existing “exchangeable goods” such as HL7 artifacts, other XML documents, and other media types (including images and other binary data) in a hierarchical structure and provides data pedigree meta data. | |
| + | |||
| + | hData records may adhere to the content required by an hData Content Profile (HCP): a content profile prescribes the required and optional content a record must provide, and allocates the place for the Section Documents within the hierarchical structure. Note that a single hData record can be compliant with multiple HCPs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | === HCP Example === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * HCP1 requires that a given hData record provides all available CCDs for a patient at /ccd within the hData record. | ||
| + | * HCP2 requires that a given hData record provide simplified allergies and current medication at /simple/allergies and /simple/meds within the hData record. | ||
| + | * HCP3 requires that available x-ray images in DICOM format are provided at /imaging/x-rays within the hData record. | ||
| + | The following record would be compliant with all three HCPs: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre>/ - | ||
| + | + /ccd | ||
| + | + /imaging/x-rays | ||
| + | - /simple - | ||
| + | + /allergies | ||
| + | - /meds | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other combinations are possible as well. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Relationship with HL7 Framework === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The illustration below was created by the ArB and annotated by hData to illustrate how hData fits into the HL7 SAIF: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Relationships among groups and artifacts - hData additions-v3.png]] |
</center> | </center> | ||
| − | == Documentation == | + | == Supporting Documentation == |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Metadata Mapping === | ||
| + | |||
| + | :This section is meant to establish a mapping between the IHE XDS Metadata, the CDA R2 Headers, and the hData Metadata model. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :{| border="1" | ||
| + | | | '''IHE XDS Metadata''' | ||
| + | | | '''CDA R2 Metadata''' | ||
| + | | | '''hData Metadata''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || availabilityStatus | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.statusCode | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || authorInstitution | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.author.representedOrganization | ||
| + | || /hrf-md:PedigreeInfo/hrf-md:Organization ? | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || authorPerson | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.author.person | ||
| + | || /hrf-md:PedigreeInfo/hrf-md:Author | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || authorRole | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.author.code(RoleCode) | ||
| + | || /hrf-md:PedigreeInfo/hrf-md:Author/@role | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || authorSpecialty | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.author.functionCode(ParticipationFunction) | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || classCode | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.code.code (duplicate of XDS/typeCode) | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || classCodeDisplayName | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.code.displayName (duplicate of XDS/typeCode) | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || confidentialityCode | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.confidentialityCode | ||
| + | || being added? | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || confidentialityCodeDisplayName | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.confidentialityCode | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || creationTime | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.effectiveTime | ||
| + | || /hrf-md:DocumentMetaData/hrf-md:RecordDate/hrf-md:CreatedDateTime | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || entryUUID | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || eventCodeList | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.documentationOf(type:ServiceEvent).code.code | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || eventCodeDisplayNameList | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.documentationOf(type:ServiceEvent).code.displayName | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || formatCode | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.text.mediaType.code | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || formatCodeDisplayName | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.text.mediaType.displayName | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || hash | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || healthcareFacilityTypeCode | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.componentOf(type:encompassingEncounter).location(type:HealthCareFacility).code.code | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || healthcareFacilityTypeCodeDisplayName | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.componentOf(type:encompassingEncounter).location(type:HealthCareFacility).code.displayName | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || legalAuthenticator | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.legalAuthenticator | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || languageCode | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.languageCode | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || mimeType | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.text.mediaType.code | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || parentDocumentRelationship | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.relatedDocument(ParentDocument).code | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || parentDocumentId | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.relatedDocument(type:ParentDocument).id | ||
| + | || /hrf-md:DocumentMetaData/hrf-md:LinkedDocuments/hrf-md:Target (no relationship type) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || patientId | ||
| + | || n/a (there is a sourcePatientId, but this isn't the same as the affinity-domain-specific patientId field) | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || practiceSettingCode | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.componentOf(type:encompassingEncounter).location(type:HealthCareFacility).code.code (duplicate of XDS/practiceSettingCode) | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || practiceSettingCode DisplayName | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.componentOf(type:encompassingEncounter).location(type:HealthCareFacility).code.displayName (duplicate of XDS/practiceSettingCode) | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| + | || serviceStartTime | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.documentationOf(type:ServiceEvent).efffectiveTime.low | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | || serviceStopTime | |
| − | + | || ClinicalDocument.documentationOf(type:ServiceEvent).efffectiveTime.high | |
| + | || n/a | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| + | || size | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| + | || sourcePatientId | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.recordTarget(type:R_patient).id | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| + | || sourcePatientInfo | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.recordTarget(type:R_patient) | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || title | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.title | ||
| + | || in atom:title | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | || typeCode | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.code.code (duplicate of XDS/classCode) | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| + | || typeCodeDisplayName | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.code.displayName (duplicate of XDS/classCode) | ||
| + | || n/a | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| + | || uniqueId | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.id | ||
| + | || /hrf-md:DocumentMetaData/hrf-md:DocumentId AND atom:id | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| + | || URI | ||
| + | || ClinicalDocument.text.reference (ED.reference can be document filename and/or URL) | ||
| + | || in atom:link | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | === | + | === Structured Document Template Design Pilot === |
| + | hData is part of the [[Structured Document Template Design Pilot]], progress can be tracked on the [[HData Template Sub Project]] page. Within this pilot it is demonstrated that hData can be made conceptually equivalent to a CDA based approach: the content of an CDA document and an hData record following the rules of the HRF specification are isomorphic, as long as an hData Content Profile is used that supports all features used in the CDA instance. | ||
| + | === Example Schemas for Simplified C32/C83 content === | ||
| − | + | Project hData initially produced a set of simplified schemas as wireformat for content (see [http://github.com/projecthdata/hData here] for more information). These schemas were derived from the content of the HITSP C83 profile of the HL7 CCD. It was not created with a rigorously defined algorithm (like greenCDA), since it was only intended to illustrate the potential benefit of simplified wireformats for a number of non-traditional applications, such as low-powered devices, rich internet applications, and other agile projects. | |
| − | + | The current hData specification '''do not''' require the simplified schemas. Instead, hData offers the HCP methods to define content profiles for domain specific use. The content profiles will use standard HL7 v3 artifacts, but may also use simplified wireformats once they become available (e.g. through greenCDA or neutral mapping). | |
| − | == | + | == References == |
| − | + | === Templates === | |
| − | + | The hData Content Profile Documentation Template can be found here: [[File:HData Content Profile Definition Template-20120210.docx]] | |
| − | + | === Presentation Material === | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[media:Security WG Presentation-v2.pptx|This]] presentation was used to illustrate the general security concept for hData. | |
| − | + | === Overview Videos === | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The MITRE Corporation has created a set of overview videos [http://www.projecthdata.org/videos.html here]. | |
| − | + | === Links === | |
| − | + | Project hData was started by MITRE and is currently hosted on http://projecthdata.org/ | |
| − | + | Historical material from the project is available [[HData/Archive|here]]. | |
Latest revision as of 14:14, 10 February 2012
Return to Main SOA WG/HSSP Page
Overview
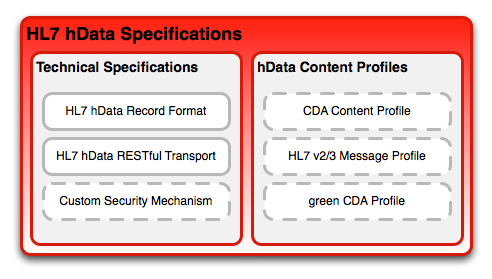
hData is a set of specifications that have been developed with ease-of-implementation in mind. hData was first presented to a wider audience within HL7 as the September 2009 meeting in Atlanta, GA. Since then, hData has first been evalauted as a HL7 research project within the ITS working group. The research project culminated in a "For Comment" ballot in January 2011. After a carefull analysis, HL7 decided to standardize hData under the leadership of the SOA working group with ITS and MnM as interested parties.
Specifications
Standardization Status
hData currently consists of two specifications which have both past the initial peer review:
- The HL7 hData Record Format V1 specifies how multiple documents (XML and non-XML media types) containing medical data can be hierarchically organized. It allows metadata management per individual document, signature over files, linking of related documents, and defines the items needed to define a complete hData Content Profile (HCP). The current project scope statement is here. The September 2011 DSTU Ballot reconciliation document can be found here.
- The hData REST Binding for RLUS V1 specifies how a record adhering to the HRF specification can be access through a RESTful approach using HTTP as the transport protocol. It is a Object Management Group (OMG) specification that was developed by the HL7/OMG HSSP collaboration.
Introduction
hData requires strong separation of the technical representation and transport technology on the one side, and the clinical content of an electronic health record on the other side. To this end, hData has the concept of hData Content Profiles (HCP), which define what kind of content is represented and transport through hData. It should be note that conceptually CDA and hData are similar in their approach to representing data points in a hierarchical way.
It should be noted that the two specification are not an ITS in the traditional sense, since they do not determine how a logical model is implemented and rendered on the wire. Instead, the HRF organizes existing “exchangeable goods” such as HL7 artifacts, other XML documents, and other media types (including images and other binary data) in a hierarchical structure and provides data pedigree meta data.
hData records may adhere to the content required by an hData Content Profile (HCP): a content profile prescribes the required and optional content a record must provide, and allocates the place for the Section Documents within the hierarchical structure. Note that a single hData record can be compliant with multiple HCPs.
HCP Example
The following record would be compliant with all three HCPs: / -
+ /ccd
+ /imaging/x-rays
- /simple -
+ /allergies
- /meds
Other combinations are possible as well. |
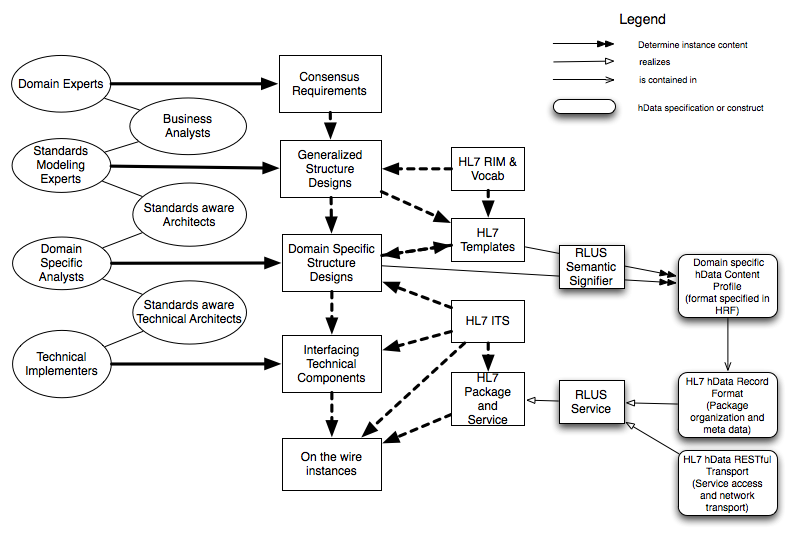
Relationship with HL7 Framework
The illustration below was created by the ArB and annotated by hData to illustrate how hData fits into the HL7 SAIF:
Supporting Documentation
Metadata Mapping
- This section is meant to establish a mapping between the IHE XDS Metadata, the CDA R2 Headers, and the hData Metadata model.
IHE XDS Metadata CDA R2 Metadata hData Metadata availabilityStatus ClinicalDocument.statusCode n/a authorInstitution ClinicalDocument.author.representedOrganization /hrf-md:PedigreeInfo/hrf-md:Organization ? authorPerson ClinicalDocument.author.person /hrf-md:PedigreeInfo/hrf-md:Author authorRole ClinicalDocument.author.code(RoleCode) /hrf-md:PedigreeInfo/hrf-md:Author/@role authorSpecialty ClinicalDocument.author.functionCode(ParticipationFunction) n/a classCode ClinicalDocument.code.code (duplicate of XDS/typeCode) n/a classCodeDisplayName ClinicalDocument.code.displayName (duplicate of XDS/typeCode) n/a confidentialityCode ClinicalDocument.confidentialityCode being added? confidentialityCodeDisplayName ClinicalDocument.confidentialityCode n/a creationTime ClinicalDocument.effectiveTime /hrf-md:DocumentMetaData/hrf-md:RecordDate/hrf-md:CreatedDateTime entryUUID n/a n/a eventCodeList ClinicalDocument.documentationOf(type:ServiceEvent).code.code n/a eventCodeDisplayNameList ClinicalDocument.documentationOf(type:ServiceEvent).code.displayName n/a formatCode ClinicalDocument.text.mediaType.code n/a formatCodeDisplayName ClinicalDocument.text.mediaType.displayName n/a hash n/a n/a healthcareFacilityTypeCode ClinicalDocument.componentOf(type:encompassingEncounter).location(type:HealthCareFacility).code.code n/a healthcareFacilityTypeCodeDisplayName ClinicalDocument.componentOf(type:encompassingEncounter).location(type:HealthCareFacility).code.displayName n/a legalAuthenticator ClinicalDocument.legalAuthenticator n/a languageCode ClinicalDocument.languageCode n/a mimeType ClinicalDocument.text.mediaType.code n/a parentDocumentRelationship ClinicalDocument.relatedDocument(ParentDocument).code n/a parentDocumentId ClinicalDocument.relatedDocument(type:ParentDocument).id /hrf-md:DocumentMetaData/hrf-md:LinkedDocuments/hrf-md:Target (no relationship type) patientId n/a (there is a sourcePatientId, but this isn't the same as the affinity-domain-specific patientId field) n/a practiceSettingCode ClinicalDocument.componentOf(type:encompassingEncounter).location(type:HealthCareFacility).code.code (duplicate of XDS/practiceSettingCode) n/a practiceSettingCode DisplayName ClinicalDocument.componentOf(type:encompassingEncounter).location(type:HealthCareFacility).code.displayName (duplicate of XDS/practiceSettingCode) n/a serviceStartTime ClinicalDocument.documentationOf(type:ServiceEvent).efffectiveTime.low n/a serviceStopTime ClinicalDocument.documentationOf(type:ServiceEvent).efffectiveTime.high n/a size n/a sourcePatientId ClinicalDocument.recordTarget(type:R_patient).id n/a sourcePatientInfo ClinicalDocument.recordTarget(type:R_patient) n/a title ClinicalDocument.title in atom:title typeCode ClinicalDocument.code.code (duplicate of XDS/classCode) n/a typeCodeDisplayName ClinicalDocument.code.displayName (duplicate of XDS/classCode) n/a uniqueId ClinicalDocument.id /hrf-md:DocumentMetaData/hrf-md:DocumentId AND atom:id URI ClinicalDocument.text.reference (ED.reference can be document filename and/or URL) in atom:link
Structured Document Template Design Pilot
hData is part of the Structured Document Template Design Pilot, progress can be tracked on the HData Template Sub Project page. Within this pilot it is demonstrated that hData can be made conceptually equivalent to a CDA based approach: the content of an CDA document and an hData record following the rules of the HRF specification are isomorphic, as long as an hData Content Profile is used that supports all features used in the CDA instance.
Example Schemas for Simplified C32/C83 content
Project hData initially produced a set of simplified schemas as wireformat for content (see here for more information). These schemas were derived from the content of the HITSP C83 profile of the HL7 CCD. It was not created with a rigorously defined algorithm (like greenCDA), since it was only intended to illustrate the potential benefit of simplified wireformats for a number of non-traditional applications, such as low-powered devices, rich internet applications, and other agile projects.
The current hData specification do not require the simplified schemas. Instead, hData offers the HCP methods to define content profiles for domain specific use. The content profiles will use standard HL7 v3 artifacts, but may also use simplified wireformats once they become available (e.g. through greenCDA or neutral mapping).
References
Templates
The hData Content Profile Documentation Template can be found here: File:HData Content Profile Definition Template-20120210.docx
Presentation Material
This presentation was used to illustrate the general security concept for hData.
Overview Videos
The MITRE Corporation has created a set of overview videos here.
Links
Project hData was started by MITRE and is currently hosted on http://projecthdata.org/
Historical material from the project is available here.