Difference between revisions of "Permissions Catalog: Recommendations for Reuse"
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==Healthcare Operations== | + | ==Healthcare Operations rather ACRUDE operations== |
| − | + | The healthcare work flow as specified in HL7, provides for "trigger events" that correspond to healthcare-specific operations: | |
* create | * create | ||
* revise | * revise | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
* nullify | * nullify | ||
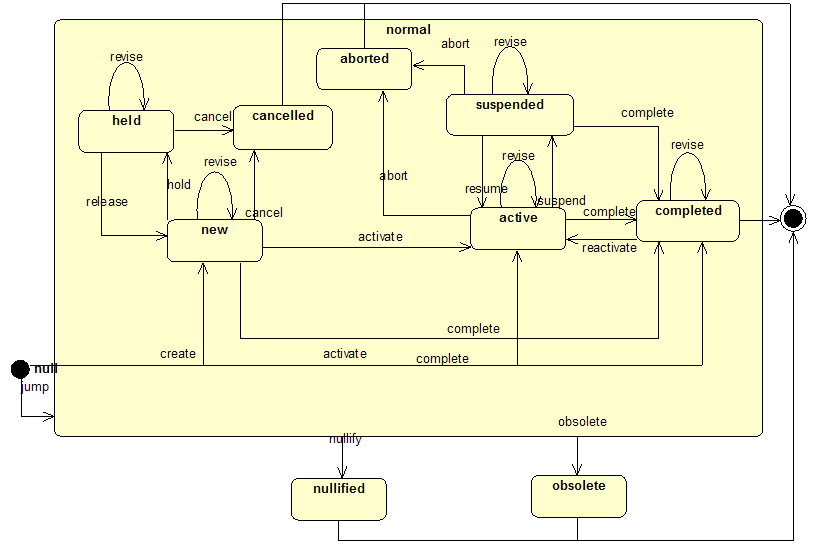
| − | + | The following diagram shows the trigger events and the states that correspond to the healthcare work flow for healthcare object (e.g. Act). For example, an order may be created, activated, then canceled. Similarly an order may be created, activate, revised, and eventually | |
[[Image:RIM ActStatus.gif]] | [[Image:RIM ActStatus.gif]] | ||
| − | |||
==Value Sets for "Object"== | ==Value Sets for "Object"== | ||
Revision as of 19:59, 25 August 2008
The current Permissions Catalog for Role-Based Access Control specifies a set of normative permissions that specify operations that may be applied to a variety of object types.
The permission catalog is a normative specification and it is available for download.
- The most recently published permission catalog is 20071112_HL7_RBAC_Healthcare_Permission_Catalog_v3_37.pdf
The operations refer to the ability to append, create, read, update, delete, and execute specific "objects" identified in the RBAC standards. The "objects specify:
| Permission | ||
|
Operation |
Object |
Effect |
|
append |
Administrative Ad-hoc Report |
A role that has this permission, allows the user that logs in with that role to append information to an existing ad-hoc administrative report. |
Healthcare Operations rather ACRUDE operations
The healthcare work flow as specified in HL7, provides for "trigger events" that correspond to healthcare-specific operations:
- create
- revise
- activate
- complete
- suspend
- resume
- abort
- hold
- release
- cancel
- obsolete
- nullify
The following diagram shows the trigger events and the states that correspond to the healthcare work flow for healthcare object (e.g. Act). For example, an order may be created, activated, then canceled. Similarly an order may be created, activate, revised, and eventually